The RPE quality control programme was divided into four distinct phases:
- Inventory/registration [3,4];
- Three types of inspection: visual, tactile and radiological [3,5,6];
- Periodicity of inspection [4, 7-9];
- Rejection or acceptance criteria [9,10].
In order to identify and classify the existing RPE's, an inventory has been developed which includes:
- The serial number;
- The unit to which they belonged;
- Model (apron, full body, skirt or vest);
- Size;
- Brand;
- Lead equivalency;
- Date of work;
- Acquisition date;
- RPE inspection date;
- Name of inspection manager.
The following documents were produced: validation checklist and hypothetical budget [3,4]. The inventory triggered the RPE briefing, which was the first step to characterise the starting point of this protocol. Then, the inspection, maintenance and replacement methodology of the programme was identified through a test essay in a hospital in the Lisbon centre. All existing RPE's were collected in the imaging department, operating room, stomatology and gastroenterology units.
For each type of inspection, the frequency and validation method of integrity were determined:
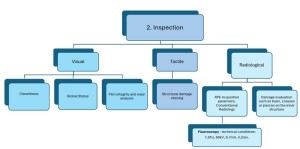
Visual inspection:
- General condition: Good maintenance, Slightly deteriorated, Extremely deteriorated;
- Cracks or damage to the external structure: Punctures or wrinkles;
- Cleaning status: Clean, Slightly Clean or Dirty;
- Film integrity and wear analysis: Inspection of straps, zips, Velcro fasteners, magnets, outer fabric and cover.
Tactile inspection:
- Check for structural damage: bends and junctions.
Radiological inspection:
- Determine the technical parameters to be used to acquire radiograms (81kV, 2.50 doses, large focus, 41.5cm x 41.5cm field of view (FOV) collimation, 1.15cm focus-film distance) with a fluoroscopic recording of the RPE's to detect internal damage, systemising the results by area [5,7,8].
Acceptance and rejection criteria were applied to the circulating RPE's after analysis of the radiological images and calculation of measures such as area or length of damage [9,10].
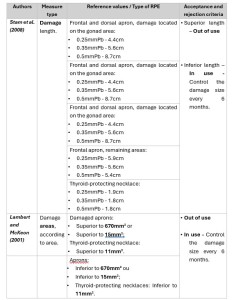
The inspection periodicity was defined according to its utility, frequency of use and the radiation source which each RPE is exposed to [4,8,9,11]. On the Gastroenterology and Operation Room units the periodicity is yearly, and on the Imageology and Stomatology units the periodicity is between 18 to 24 months. In case there is any kind of damage to the RPE’s, this control is processed every 6 months.
The non-conformities were registered and, a finally a report was elaborated, which contained future recommendations and guidelines, assuming the form of a Best Practices Guide.
In order to verify the accuracy of the RPE’s attenuation effect on radiation emissions, the percentage of radiation attenuation was calculated on three randomly selected aprons and three randomly selected thyroid-protecting necklaces with different lead equivalence (0.25mmPb, 0.35mmPb and 0.5mmPb), using 42 thermoluminescent dosimeters, exposed to the X ray beams. Based on studies from Papadopoulos et al. and Konig et al. [12,13], the following technical conditions were used: 60kVp, 90kVp and 121kVp, 32mAs; Field of View 41,5x41,5cm; Focus-film distance 115cm. Besides the experimental value report, these values were compared to simulation calculated values using the Microsoft Excel program [2,11–14]. The measurement’s geometry was purposely constant in all exposures, in order to create an environment with the same conditions on both situations.