Coronary artery disease (CAD) commonly develops owing to the formation of plaques within the walls of the coronary arteries, which reduces blood flow and can lead to serious complications such as myocardial ischemia and infarction [1].
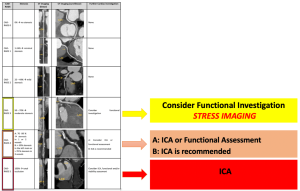
Based on the current recommendations, patients with cardiac risk candidate for cardiac and noncardiac surgery at intermediate-high risk are sent to invasive coronary angiography (ICA) (I class indication) for assessing CAD [2,3]. The indication to Coronary Computed Tomography (CCT) is growing as a promising alternative in the evaluation of CAD before surgery. CCT has demonstrated high diagnostic accuracy in the non-invasive rule out of the patients with a significant CAD thanks to its high negative predict value. [Fugure 1]