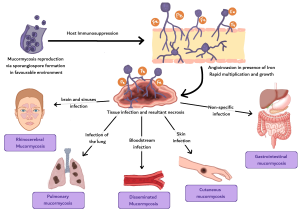
Mucormycosis is a rapidly progressive, angioinvasive fungal infection caused by organisms of the order Mucorales, most commonly Rhizopus and Mucor. It predominantly affects immunocompromised patients, with major risk factors including uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, hematologic malignancy, stem cell or solid organ transplantation, prolonged neutropenia, corticosteroid therapy, and deferoxamine use.
Infection follows inhalation, ingestion, or direct inoculation of fungal spores. Marked angioinvasion leads to vascular thrombosis, tissue ischemia, and necrosis, with rapid spread along vascular, neural, and contiguous tissue planes, accounting for the aggressive clinical course and high mortality (1). Microscopy shows broad, ribbon-like, pauciseptate hyphae with right-angle branching.