Congress:
ECR25
Poster Number:
C-22137
Type:
Poster: EPOS Radiologist (educational)
Authorblock:
I. Yaşar, F. Ozdemir, C. Turan Bektaş, I. T. Rakıcı, H. Özdemir, A. S. Mahmutoglu; Istanbul/TR
Disclosures:
Irem Yaşar:
Nothing to disclose
Firat Ozdemir:
Nothing to disclose
Ceyda Turan Bektaş:
Nothing to disclose
Ibrahim Taşkın Rakıcı:
Nothing to disclose
Hanife Özdemir:
Nothing to disclose
Abdullah Soydan Mahmutoglu:
Nothing to disclose
Keywords:
Lung, Respiratory system, CT, Screening, Cancer, Cysts, Neoplasia
To define the Lung-RADS category, the lesions are characterized as either parenchymal nodules, airway nodules, or atypical cystic lesions[1-4]. The Lung-RADS score is then calculated by categorizing these lesions based on size and growth. The LDCT exam is considered Lung RADS 0 if the prior chest exam is absent or being located for comparison, if there are parts of the lungs that cannot be evaluated, or if there are findings suggesting an inflammatory or infectious process.
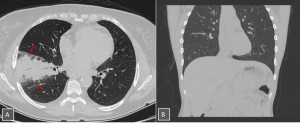
Fig 1: Fig. 1: Examples of Lung-RADS 0 CT scans. (A) Findings suggesting an infectious process (consolidation and air bronchograms) are seen in the right lung. (B) Upper zones of the lungs are not included in the scan.
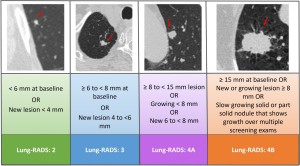
Fig 2: Fig. 2 : Lung-RADS classification of solid nodules.
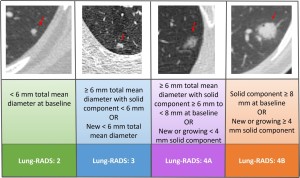
Fig 3: Fig. 3 : Lung-RADS classification of part solid nodules.
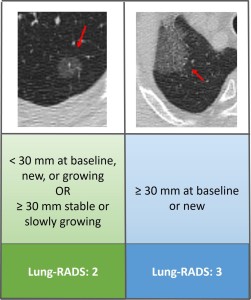
Fig 4: Fig. 4 : Lung-RADS classification of ground glass nodules (GGNs).
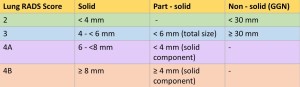
Fig 5: Fig. 5: Size thresholds for new or growing nodules for different nodule categories.
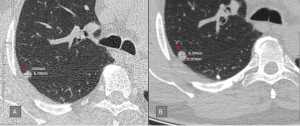
Fig 6: Fig. 6: Size growth in a solid nodule. Initial scan (A) shows a category 3 nodule (mean size : 7,1 mm). The nodule is upgraded to category 4B (mean size: 9,7 mm) in the follow-up scan(B).
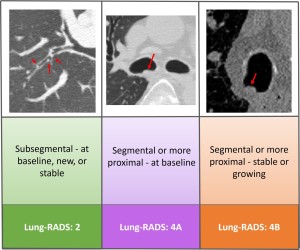
Fig 7: Fig. 7 : Lung-RADS classification of airway nodules.
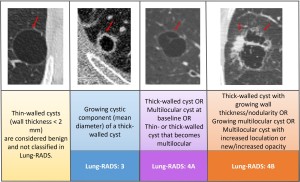
Fig 8: Fig. 8 : Lung-RADS classification of atypical pulmonary cysts.
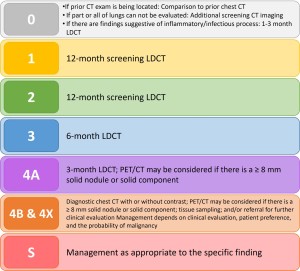
Fig 9: Fig. 9: Management recommendations according to Lung-RADS categories.
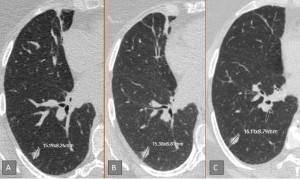
Fig 10: Fig. 10: Slow-growing solid nodule. The patient had a solid nodule with a mean diameter of 11,7 mm (Lung-RADS 4A) in the right lung in her initial screening CT (A). In follow-up CT scans taken 6 months apart (B,C) the nodule showed minimal growth (0,3 mm) . The final score was determined as Lung RADS 4B.
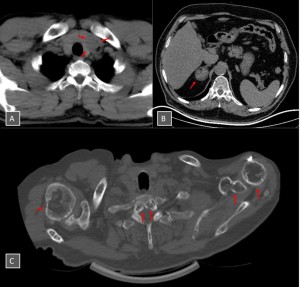
Fig 11: Fig. 11: Examples of Lung-RADS S modifiers. (A) Hypodense thyroid nodule seen in the left thyroid lobe, (B) right adrenal mass included in the field of view , and (C) multiple lytic lesions in the bones are visible in the screening scans(red arrows).