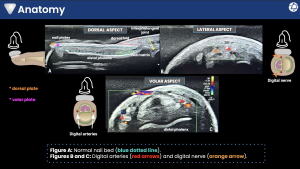
High-frequency ultrasound has become an established tool for evaluating hand and finger pathology, offering real-time, high-resolution assessment of superficial soft tissues. The use of linear transducers operating at frequencies ≥15–22 MHz enables detailed visualization of the nail unit, digital nerves, vessels, tendons, and subcutaneous structures.
This work is based on a retrospective pictorial review of patients referred for ultrasound evaluation of palpable or symptomatic finger lesions. All examinations were performed using high-frequency linear transducers, with systematic assessment including:
-
Lesion location (subungual, periungual, volar, dorsal, lateral)
-
Size, shape, margins, and echogenicity
-
Relationship to adjacent structures (nerves, joints, nail matrix, tendons)
-
Presence of posterior acoustic features
-
Vascularity assessed with color and power Doppler
Selected cases were correlated with clinical findings or additional imaging when available.
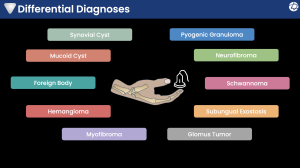
The reviewed spectrum of lesions includes:
-
Synovial cysts and mucoid cysts
-
Vascular lesions (hemangioma, pyogenic granuloma, glomus tumor)
-
Peripheral nerve sheath tumors (schwannoma and neurofibroma)
-
Myofibroma
-
Foreign body
-
Subungual exostosis