Transvaginal ultrasonography is a very important and accessible tool for the diagnosis of endometriosis. It allows insights into the affected areas and the severity of the disease by focusing on the most commonly anatomical regions involved in DE in symptomatic patients.
The Society of Radiologists in Ultrasound Consensus on Routine Pelvic US for Endometriosis, in its recommendations, advocates for a systematic and detailed ultrasound examination of the pelvis, including the structures described in the previous sector, categorizing them in 3 categories - direct findings, indirect findings and possibly associated - according to its association with endometriosis.
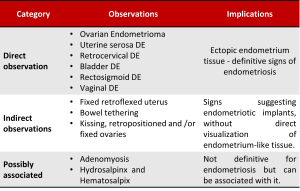
According to the number of suggestive findings of endometriosis, or its absence, the examiner can infer the probability of the patient having endometriosis, diagnose it or exclude the disease. 
Patients at high risk for endometriosis may benefit from proceeding directly to advanced imaging studies, such as magnetic resonance imaging particularly in cases of planned surgical treatment and monitoring and medical management for infertility.