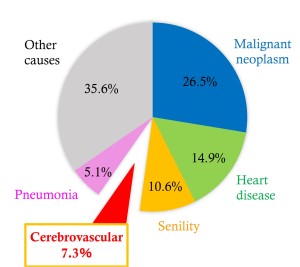
In Japan, cerebrovascular disease is the fourth cause of death and the first cause of bedridden patients [1]. Recently, cerebral stroke has been under serious consideration due to the westernization of the diets and an increase in geriatric diseases. At present, cerebral stroke is still one of the most important diseases to control and prevent (Fig.1).
To establish a method for image-based diagnosis of cerebral stroke, the authors developed a phantom that could correctly evaluate disease detection by image-prodessing and that could vizualize disease using X-ray CT imaging, while evaluating the imaging conditions [2-5]. Visualization of acute cerebral infarction wihtin 4.5 hours, after the development of cerebral infarction is essential because it is the time index used to judge whether thrombolytic therapy with use of rt-PA is applicable [6]. Traditionally, it has been difficult to vizualize acute cerebral infarction from images produced by X-ray CT [7].
photon-counting CT, which has recently appeared in clinical practice, can convert photons directly into electrical signals by introducing semiconductors (cadmium telluride) instead of conventional integrating detectors that use scintillators and photodiodes. We focused on this technology because it is expected to improve low-contrast detection performance by preserving energy information and increasing dose-utilization efficiency due to reduced electrical noise [8].
We applied photon-counting detector CT images to a cerebral infarction phantom developed using to visualize acute ischemic stroke, and evaluation of image quality was exmined using a detectability index (d'2), CNRLO and figure of merit (FOM).