Congress:
ECR25
Poster Number:
C-17860
Type:
Poster: EPOS Radiologist (scientific)
Authorblock:
X. Zhang1, G. Zhang1, H. Sun1, Z. Jin1, J. Yan1, M. Xu1, L. Xu2, J. Zhang1, X. Bai1; 1Beijing/CN, 2Hangzhou/CN
Disclosures:
Xiaoxiao Zhang:
Nothing to disclose
Gumuyang Zhang:
Nothing to disclose
Hao Sun:
Nothing to disclose
Zhengyu Jin:
Nothing to disclose
Jing Yan:
Nothing to disclose
Min Xu:
Nothing to disclose
Lili Xu:
Nothing to disclose
Jiahui Zhang:
Nothing to disclose
Xin Bai:
Nothing to disclose
Keywords:
Abdomen, Kidney, Urinary Tract / Bladder, CT, Technology assessment, Calcifications / Calculi
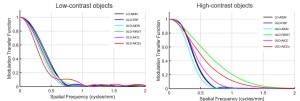
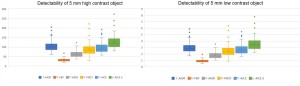
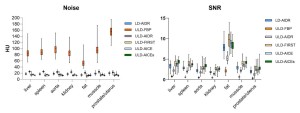
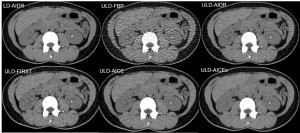
In the phantom images, ULD-AICEs exhibited superior detectability of high and low contrast object in all size compared to LD-AIDR images or other ULD images (P < 0.01).