175 steatotic patients were included after ethics approval for liver MASLD assessment using ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging. Seventy-five adults were included from the RHU QUIDNASH study funded by the National Agency for Research (ANR-17- RHUS-0009). One hundred teenagers were included and underwent ultrasound examination including US-ATI and SWE.
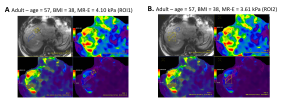
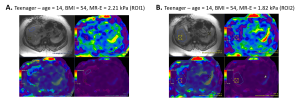
For each patient, MR-PDFF was calculated using an IDEAL-IQ sequence while MR-E measurements were achieved with the MR-Touch sequence, using the Resoundant device at 60 Hz, on GE 1.5 T Artist magnetic resonance scanner. MR measurements were performed on five different slices using two ROIs: (ROI1), >350 mm located anteriorly at the site of ultrasound measurements and (ROI2), the largest area available at mid-liver, avoiding vessels and artifacts, corresponding to recommendations.
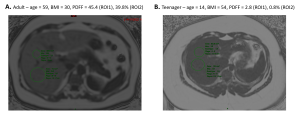
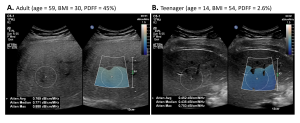
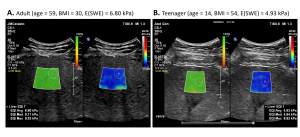
An ultrasound examination was also performed using the Epiq Elite system (Philips US, Bothell, USA) using ElastQ and LFQ features for SWE and attenuation measurements, respectively. Five stiffness measurements and three attenuation measurements were collected at least 1 cm below the liver capsule on a large ROI encompassing the liver (ROI1).
The variability of intrinsic measurements was calculated using three coefficients: the interquartile range /median (VC1%) and two different variation coefficients VC2% (standard deviation/mean) and VC3% ((max – min) / mean). Wilcoxon signed-rank statistical tests were performed to assess whether variabilities were different between modalities and regions of interests, and Mann-Whitney tests were computed to assess whether variabilities were different between the populations (full cohort, teenagers and adults).