The study demonstrates the possibility of adopting a Natural Language Processing (NLP) model, pre-trained on Italian language data and openly available, for use in a local offline framework for the classification of chest CT reports written in the Italian language. 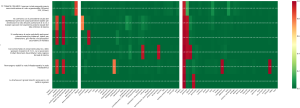
This work underscores the feasibility of integrating such an AI-based system into radiology, particularly in a context like Italian healthcare, where unstructured reporting is common.
Furthermore, the continued development of similar models could significantly enhance the value of textual data and, subsequently, the images contained within digital radiology archives.
This advancement opens up the possibility of leveraging these data to train AI systems for image recognition or to define diagnostic and therapeutic pathways.