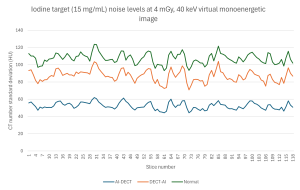
The noise levels in all targets and maps decreased significantly (p < 0.05), by a mean reduction of 28 HU, in the two AI noise-reduced image sets compared to the images with no AI noise reduction. Noise reduction was greater, by 6 HU on average, in images in which AI noise reduction was applied to the X-ray tube A and B data than when it was applied to the DECT maps with a few exceptions across specific phantom targets and maps. In the images with X-ray tube A and B data noise reduction the noise was from 5 to 136 HU (mean 31 HU) lower than in the images with no AI noise reduction. The images with DECT map noise reduction had 3 to 95 HU (mean 25 HU) lower noise than the images with no AI noise reduction. An example of the different noise levels of an iodine target in a subtraction image across the phantom z axis (all slices included) is shown in Figure 2.