Congress:
ECR25
Poster Number:
C-21700
Type:
Poster: EPOS Radiologist (scientific)
Authorblock:
A. Choux1, Z. Yin2, C. L. Kim2, A. Pourmorteza1; 1Atlanta, GA, GA/US, 2Niskayuna, NY/US
Disclosures:
Arnaud Choux:
Research/Grant Support: GE HealthCare
Zhye Yin:
Employee: GE HealthCare
Chang Lyong Kim:
Employee: GE HealthCare
Amir Pourmorteza:
Grant Recipient: GE HealthCare
Keywords:
Computer applications, CT, CT-Angiography, CT-Quantitative, Physics, Cancer
Capturing the K-edge of CAs significantly (t-test, p<0.01) improved the spectral separability of iodine from gadolinium (15.3° vs 19.5°), bismuth (6.1° vs 9.5°), and tantalum (14.2° vs 29.3°) for setting1 vs setting2. Furthermore, blood-CA separability was increased for all CAs with setting2.
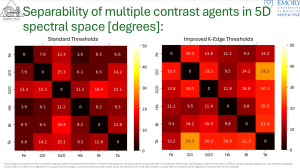
Fig 3: Spectral separability of different contrast agents using standard (left) and improved (right) K-Edge threshold settings.
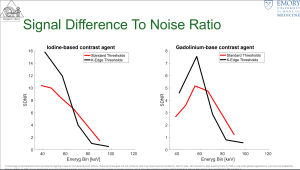
Fig 4: Signal difference to noise ratio for each energy bin for iodine-based contrast agents (left) and gadolinium-based contrast agents (right) for standard (red) and K-Edge improved (black) energy threshold settings.