
Congress:
ECR26
Poster Number:
C-10288
Type:
Poster: EPOS Radiographer (scientific)
Authorblock:
S. Kawauchi1, K. Chida2, Y. Hamada1, T. Moritake3, W. Tsuruta4; 1Minato-Ku/JP, 2Sendai/JP, 3Chiba/JP, 4Tokyo/JP
Disclosures:
Satoru Kawauchi:
Nothing to disclose
Koichi Chida:
Nothing to disclose
Yusuke Hamada:
Nothing to disclose
Takashi Moritake:
Nothing to disclose
Wataro Tsuruta:
Nothing to disclose
Keywords:
Head and neck, Neuroradiology brain, Radioprotection / Radiation dose, Catheter arteriography, Dosimetry, Embolisation, Aneurysms
Patient and Aneurysm Characteristics (table 1 and table 2)
- 183 patients (68.3% female), mean age 62.0 ± 12.8 years.
- 155 aneurysms (79.4%) in the anterior circulation; 40 (20.6%) in the posterior circulation.
- 171 patients (90.0%) had a single aneurysm; 12 had multiple.
- Intracranial stents such as neck-bridge stent for coil embolization and flow diverter stent were used in 106 patients (57.9%).
Radiation Dose Parameters (table 1)
- Mean TFT: 44.2 ± 23.1 min
- Mean Ka,r: 2.17 ± 1.18 Gy
- Mean PKA: 153.8 ± 103.2 Gy·cm²
- Mean Ka,r ratio: 1.92 ± 0.64
- Mean PSD: 0.96 ± 0.52 Gy
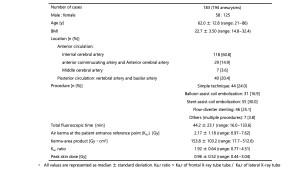
Table 1: Patient demographics, aneurysm characteristics and radiation dose characteristics.
Ka,r ratio = Ka,r of frontal X-ray tube tube / Ka,r of lateral X-ray tube
PSD Location (figure 5)
PSD location distribution:
- Occipital region: 129 cases (70.5%)
- Temporal region: 54 cases (29.5%)
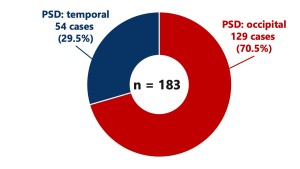
Fig 5: Breakdown of PSD location in NET. The PSD was located in the occipital region in 129 cases (70.5%) and the temporal region in 54 cases (29.5%).
Predictive Factors for Occipital PSD (table 2)
Univariate analysis:
- Male sex: odds ratio [OR] = 2.24; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.08−4.95; p = 0.0289
- Posterior circulation aneurysm: OR = 3.20; 95% CI, 1.27−9.82; p = 0.0123
- Ka,r ratio > 1.6: OR = 4.06; 95% CI, 2.04−8.21; p < 0.001
Multivariate analysis:
- Non-stent use: OR = 2.56; 95% CI, 1.22−5.65; p = 0.0125
- Ka,r ratio > 1.6: OR = 5.05; 95% CI, 2.39−11.1; p < 0.0001
These two parameters were the strongest independent predictors of occipital PSD.
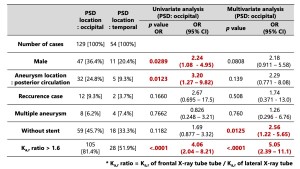
Table 2: Univariate and multivariate analyses of PSD location.
Univariate logistic analysis showed that male sex, posterior circulation aneurysm and Ka,r ratio > 1.6 were significantly associated with the occipital PSD.
Multivariate logistic analysis showed that the non-stent use and ka,r ratio > 1.6 remained independent, significant predictors for the PSD occurring in the occipital region.
Representative case (figure 6)
A man in his 60s with an unruptured basilar tip aneurysm underwent coil embolization using a double-catheter technique without intracranial stent. The Ka,r was 2.63 mGy for the frontal X-ray tube and 0.79 mGy for the lateral X-ray tube. The resulting Ka,r ratio was 3.32, exceeding the threshold value of 1.6. The PSD was observed in the occipital region (No. 27), with a measured dose of 1.74 mGy.
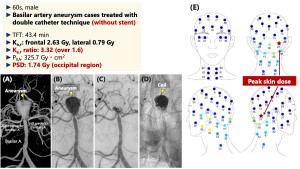
Fig 6: Representative case of occipital PSD in a non-stent NET procedure. The Ka,r ratio was 3.32 (over 1.6), and the PSD was observed at the occipital region (No. 27).
(A) Three-dimentional rotation angiography image
(B) DSA image (working projection): pre embolization
(C) DSA image (working projection): post embolization
(D) Non-DSA image (working projection): post embolization
(D): Skin dose distribution map obtained from direct measurement system. PSD was located in occipital region (No. 27)