Congress:
ECR25
Poster Number:
C-12308
Type:
Poster: EPOS Radiographer (educational)
Authorblock:
W. Y. Jeong, H. C. Park, H. J. Kim; Gwangju/KR
Disclosures:
Won Young Jeong:
Nothing to disclose
Ho Chun Park:
Nothing to disclose
Hyo Jung Kim:
Nothing to disclose
Keywords:
Thorax, CT, Radiation therapy / Oncology, Radiotherapy techniques
All treatment plans met the PTV criteria, demonstrating a uniform dose distribution. The average dose to the heart was 5.80 Gy for fVMAT, 6.97 Gy for pVMAT, and 7.60 Gy for ncVMAT, with fVMAT showing the lowest dose, which was statistically significant (p<0.001). In contrast, the average dose to the lungs was 9.01 Gy for fVMAT, 7.71 Gy for pVMAT, and 7.12 Gy for ncVMAT. The V5Gy (%) values were 52.22%, 38.61%, and 36.35%, while the V10Gy (%) values were 37.80%, 27.33%, and 24.15%, respectively. ncVMAT showed the lowest values, while fVMAT had the highest, with statistical significance (p<0.001).
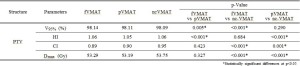
Fig 4: Results of dosimetric parameters of PTV between fVMAT, pVMAT and ncVMAT.
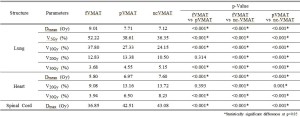
Fig 5: Results of dosimetric parameters of OARs between fVMAT, pVMAT and ncVMAT.

Fig 6: Results of dosimetric parameters of Total MU between fVMAT, pVMAT and ncVMAT.
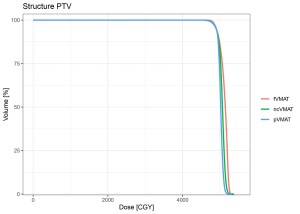
Fig 7: Comparison of PTV DVHs.

Fig 8: Comparison of Lung DVHs.
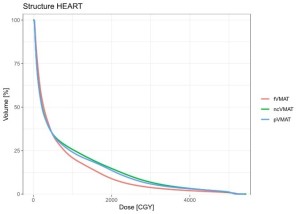
Fig 9: Comparison of Heart DVHs.
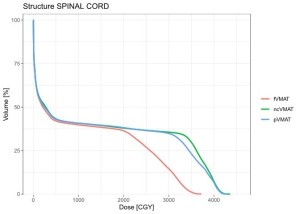
Fig 10: Comparison of Spinal Cord DVHs.