Acute pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE), a potentially life-threatening condition, occurs when an embolus, typically originating from thrombosis in the deep veins of the lower limbs, obstructs the pulmonary arterial circulation. This obstruction can lead to right heart failure, pulmonary infarction, and even sudden death. Prognosis varies widely depending on the severity of the embolism and the patient’s comorbidities. Treatment strategies range from anticoagulation in stable patients to thrombolysis or surgical embolectomy for patients with massive or high-risk PTE, thus emphasizing the need for rapid diagnosis and intervention.
The diagnostic workup for PTE necessitates a multi-faceted approach. Definitive diagnosis relies on imaging modalities. CT pulmonary angiography (CTPA) serves as the primary gold standard imaging technique, offering high sensitivity and specificity for detecting pulmonary emboli. However, it comes with its limitations of exposure to a relatively higher radiation dose, requirement of injection of iodinated intravenous contrast agent and shifting of the patient to the CT suite irrespective of the patient’s condition. Transthoracic 2D Echocardiography (TTE) plays a key role in evaluating right ventricular function and risk stratification. While not directly visualizing the embolus, it can offer prognostic insights and raise a red flag identifying patients who require further evaluation with a CTPA.
Dynamic digital radiography (DDR), a novel functional x-ray imaging modality, employs a flat-panel detector and a pulsed x-ray source.

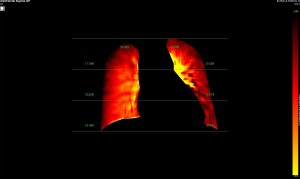
Leveraging conventional x-ray technology, DDR can be easily integrated into routine radiographic workflows alongside standard chest x-rays. DDR offers significantly reduced examination time and radiation exposure as compared to CTPA. A 10-second DDR exposure in the supine position delivers a radiation dose of just 0.13 mSv. While variations in scan parameters might slightly elevate this dose, it remains substantially lower than the radiation dose associated with CTPA.
This prospective cross sectional study was done to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of DDR with CTPA as gold standard, focusing on its potential as a screening modality for patients suspected to have PTE. DDR offers several advantages, including:
- Reduced patient radiation dose burden.
- Increased patient compliance: Shorter breath holds minimize patient discomfort.
- Enhanced patient safety:Eliminates the risk of contrast-induced nephropathy.
- Unique assessment of pulmonary perfusion: Provides valuable information of perfusion percentages in the both upper, mid and lower pulmonary zones not readily available with CTPA.
We also compared the diagnostic accuracy of DDR with transthoracic 2D echocardiography (TTE) with CTPA as gold standard as our secondary objective.