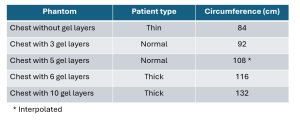
A phantom-based study was executed to evaluate the effect of body habitus on DTS and radiography, using a multipurpose chest phantom N1 “Lungman” (Kyoto Kagaku, Japan). Soft tissue thickness simulating up to 95 percentile of the USA population dimensions (circumference) was obtained by adding increasing numbers of gel layers (Bolux-I, Action Products Inc, USA, a tissue-equivalent flexible material with a physical density of approximately 1.03g/cc)1. All gel layers were positioned on the “anterior chest wall”. Chests/lungs simulations were done with 0/5/10 gel layers (Fig.1). Thoracic skeleton simulations were done similarly, adding 0/3/6/10 gel layers. Both DTS and radiographs were performed for each setup, with protocol adjusted to the "body habitus" of the phantom. Two nodules from the simulated nodule kit (Kyoto Kagaku, Japan) were embedded in the phantom prior to the chest/lung scans.

For calculation of total circumference, lateral gel layers were added to simulate the thickness of the lateral soft tissues. The total circumference was calculated as follows: for the 0 and 3 anterior gel layers no additional waist fat was added, for 6 anterior gel layers 2 side gel layers on each side were added (adding 15 cm) and for the 10 anterior gel layers 3 side layers were added on each side (adding 22 cm) (Table 1). The circumference of the chest with 5 gel layers was interpolated.
The circumferences were compared based on the information supplied by the Anthropometric Reference Data for Children and Adults United States 2015–2018, NATIONAL CENTER FOR HEALTH STATISTICS. As the statistics are divided into different age groups, the 95 percentile of the population slightly varies. The waist circumference that represents up to 95% of the USA BMI population is 126.7-136 cm for adult men and 119-133.6 cm for adult women.
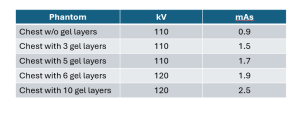
Conventional radiographs were obtained with Carestream Health DRX evolution using routine protocols and automatic exposure (Table 2).
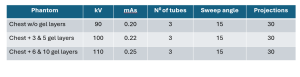
DTS images were acquired using Nanox.ARC, a stationary, floor-mounted, cold cathode, multi-source DTS system. Acquisition parameters of the DTS are detailed in table 3.
Detection of the lung nodules was evaluated on the chest/lung studies. Qualitative evaluation of the costovertebral joints was performed in the thoracic skeleton studies. These joints are posterior structures that might be difficult to detect on a conventional radiograph and are distant from the source.