Congress:
ECR25
Poster Number:
C-10875
Type:
Poster: EPOS Radiologist (scientific)
Authorblock:
K. F. Luchsinger De La Harpe, E. Horvath; Santiago/CL
Disclosures:
Kristel Francine Luchsinger De La Harpe:
Nothing to disclose
Eleonora Horvath:
Nothing to disclose
Keywords:
Breast, Mammography, Ultrasound, Biopsy, Cancer, Tissue characterisation
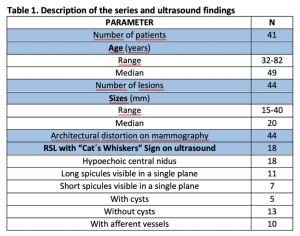
We evaluated 44 lesions (median size: 20 mm, range: 15-40 mm) in 41 patients (median age: 49 years, range: 32-82) (Table 1)
The “Cat´s Whiskers” Sign manifested itself as a composite image of a central nidus and long spicules (more frequently) converging towards it from both sides, which are only visible in a single plane because the lesion is flat (Figure 3-4-5) [4]
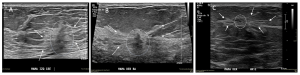
Fig 3: “Cat´s Whiskers” Sign (A, B and C): central nidus (dotted circle) with a hypoechoic non-mass type lesion, and long spicules (arrows) that converge towards it.
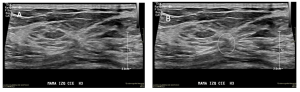
Fig 4: “Cat´s Whiskers” Sign (A and B): more subtle central nidus (dotted circle), with a hypoechoic non-mass type lesion, and shorter spicules (dotted outline) that converge towards it.

Fig 5: “Cat's Whiskers” Sign: The cat's nose represents the central nidus (dotted circle) of the lesion, and the whiskers correspond to the spicules (dotted lines) that converge on it.
The central zone was variable: heterogeneous, slightly hypoechoic, it was associated with microcysts in N=5 (11.4%) (Figure 6) [4]
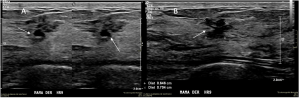
Fig 6: “Cat´s Whisker” Sign: Architectural distortion associated with the presence of cysts (arrows).
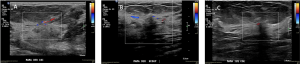
Fig 7: Doppler sign (A, B and C): The lesions show afferent vessels on color Doppler study
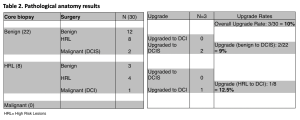
We accessed the surgical outcomes of 30 lesions of which N=22 (73%) remained benign and an HRL was found in N=8 (27%). After surgery, underestimation occurred in 10% (3 lesions: 2 DCIS and 1 ICD) (Table 2)