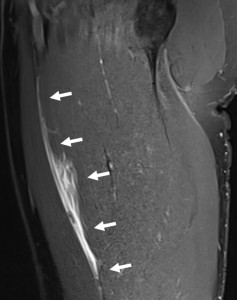
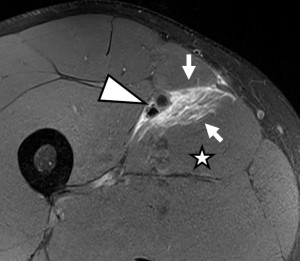
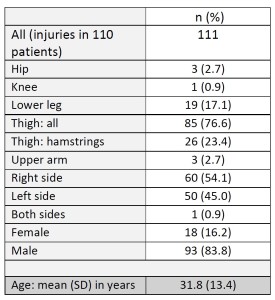
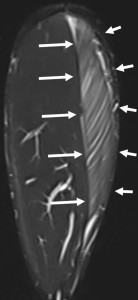
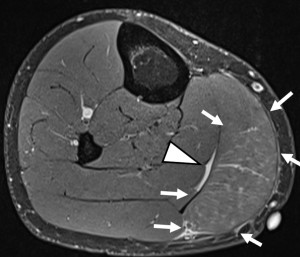
One hundred eleven acute muscle injuries in 110 patients (85% male) were assessed. Injured muscle groups included 85 thigh injuries (44 hamstring, 41 non-hamstring), 19 lower leg injuries, and 7 injuries in other locations (see Table 1 for patients`characteristics). Example cases can be seen in Figures 6-11.
Kappa values (95% confidence interval) were as follows: 0.506 (0.499, 0.514) for BAMIC, 0.566 (0.549, 0.584) for the Munich Consensus Injury Classification, and 0.306 (0.302, 0.311) for the Chan et al. Classification. The highest reproducibility was observed for hamstring injuries using the Munich Consensus Injury Classification (0.587, 0.560, 0.613), while the lowest was for lower leg injuries using the Chan et al. Classification (0.199, 0.185, 0.213). For detailed results see Tables 2 and 3.

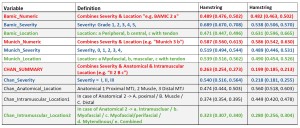
Most injuries were classified as Grade 2b (n = 31, 27.9%) in the BAMIC classification. In the Munich Consensus Injury Classification, indirect muscle injuries Grade 3B (n = 52, 46.8%) were the most frequently assigned category.
Using the Chan et al. Classification, the most frequently assigned ratings were severity Grade II (n = 76, 68.5%) and location in the muscle center (type 2, not at the myotendinous junction). Among type 2 lesions, injuries were most commonly observed in the middle and distal part of the muscle, specifically in the intramuscular location 1 types B (25.2%) and C (20.7%). For intramuscular location 2, edema in the myotendinous zone (19.8%) was most often seen.